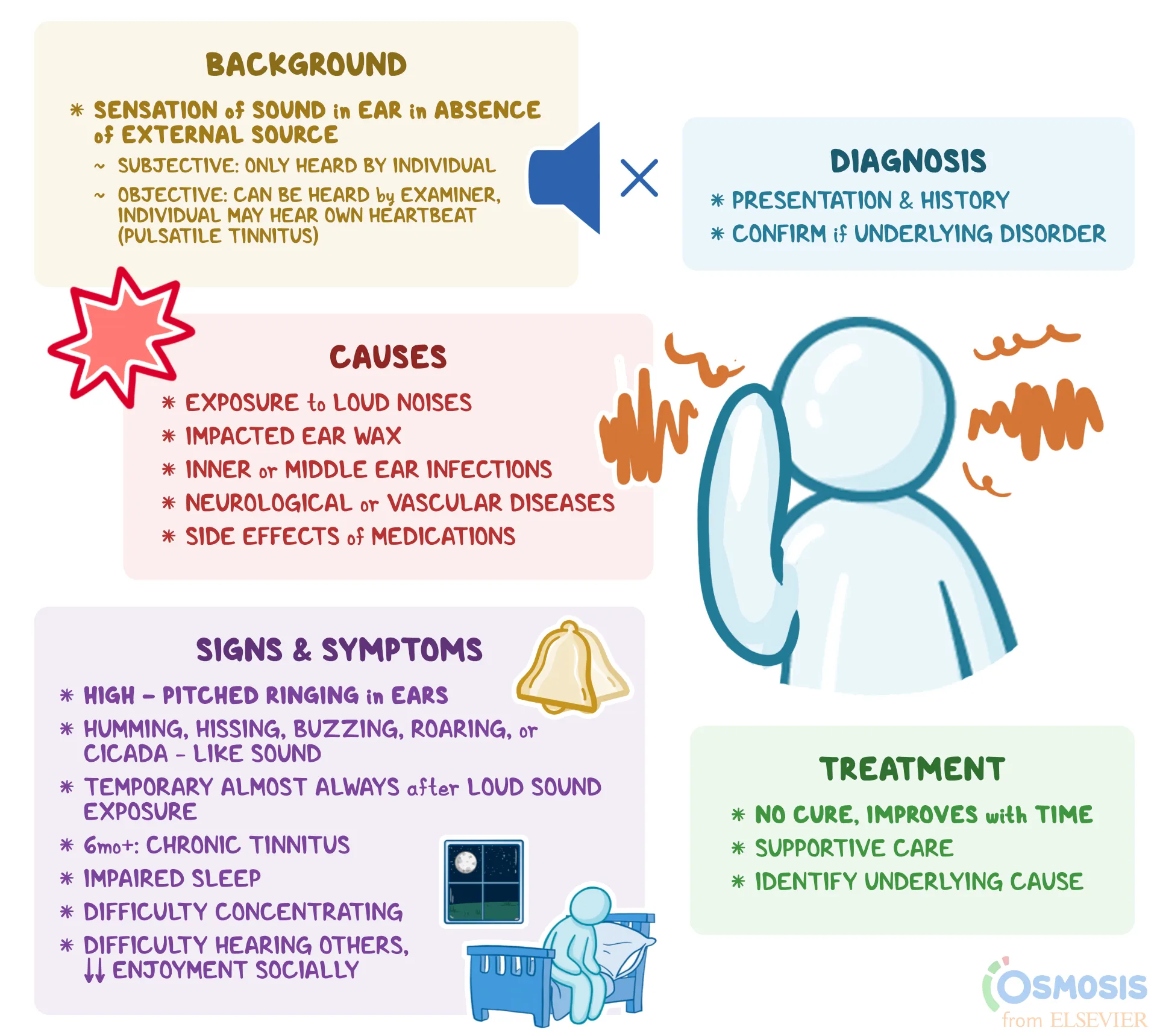
Tinnitus is a condition affecting millions globally, often described as the perception of ringing, buzzing, or hissing sounds in the ears. Though not a disease, tinnitus can indicate underlying auditory system issues or broader health concerns. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and management options can help alleviate the discomfort associated with it.
Credit Infographic: https://www.nidcd.nih.gov/
What is Tinnitus?
Tinnitus refers to the perception of sound without an external source. These phantom sounds can vary in pitch, volume, and frequency. For some, it’s a mild annoyance, while others find it significantly disruptive to their daily lives.
Causes of Tinnitus
Tinnitus can arise due to several underlying factors, including:
- Hearing Loss: Age-related hearing loss is a common cause, as damaged hair cells in the inner ear send faulty signals to the brain.
- Exposure to Loud Noise: Prolonged exposure to loud sounds, such as music, machinery, or gunfire, can damage the inner ear and lead to tinnitus.
- Earwax Blockage: Excessive earwax can accumulate and press against the eardrum, causing tinnitus.
- Ear Infections: Infections or blockages in the ear canal can alter pressure and trigger tinnitus.
- Ototoxic Medications: Certain drugs, such as antibiotics or chemotherapy agents, can damage the auditory system and cause tinnitus.
Symptoms of Tinnitus
The main symptom of tinnitus is hearing sounds that aren’t present in the environment. These sounds can be described as:
- Ringing
- Buzzing
- Hissing
- Clicking
Tinnitus can be perceived in one ear, both ears, or in the head. For some, it may be a constant sound, while others experience it intermittently.
Types of Tinnitus
Tinnitus is typically classified into two types:
- Subjective Tinnitus: The most common form, where only the individual can hear the noise. It’s usually related to problems in the ear, auditory nerves, or brain.
- Objective Tinnitus: A rare type of tinnitus where the sound can also be detected by a doctor during an examination. This is often due to issues with blood vessels or muscle contractions.
Diagnosing Tinnitus
To diagnose tinnitus, a healthcare provider will conduct a thorough examination, which may include hearing tests (audiometry) and imaging tests (MRI or CT scans) to rule out structural problems.
| Diagnostic Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Audiometry | A hearing test that helps evaluate the extent of hearing loss and detect issues with sound perception. |
| Imaging Tests | MRIs or CT scans may be used to identify abnormalities in the ear or brain. |
Treatment Options for Tinnitus
While there is no definitive cure for tinnitus, several treatment approaches can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life:
- Hearing Aids: For those with hearing loss, hearing aids can amplify external sounds, making tinnitus less noticeable.
- Sound Therapy: This involves using background noise (white noise, soft music, or nature sounds) to mask the tinnitus sound.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT helps patients cope with the emotional distress caused by tinnitus, training them to manage their focus and reduce anxiety.
- Medications: Some medications, such as antidepressants, may help reduce the severity of tinnitus, though they do not address the underlying cause.
- Lifestyle Changes: Reducing stress, avoiding loud environments, and maintaining overall ear health can help manage symptoms.
How to Cope with Tinnitus
Living with tinnitus can be challenging, but adopting certain coping strategies can help:
- Stay engaged in social activities to avoid isolating yourself due to tinnitus symptoms.
- Practice mindfulness and relaxation techniques to manage stress and reduce focus on tinnitus.
- Use sound machines or fans at night to create a low-level background noise, making tinnitus less noticeable in quiet environments.
Preventing Tinnitus
Taking preventive measures can help reduce the risk of developing tinnitus. Consider the following steps:
- Avoid exposure to loud noises by using ear protection at concerts, while using power tools, or in other noisy environments.
- Keep the volume low when using headphones or earphones.
- Take regular breaks if you’re exposed to loud environments for extended periods.
Resources for Tinnitus Support
If you or a loved one is experiencing tinnitus, it’s essential to seek professional advice. For more in-depth resources and guidance on managing tinnitus, visit Take on Tinnitus. This website provides detailed information and support for those dealing with the condition.
Conclusion
Tinnitus can be a frustrating and sometimes overwhelming condition. However, by understanding its causes, symptoms, and management options, individuals can take steps to improve their quality of life. From hearing aids and sound therapy to cognitive behavioral strategies, many solutions exist to help manage tinnitus. If you’re concerned about your symptoms, consult a healthcare professional to explore the best course of action.